What is a KPI?
KPI stands for key performance indicator, a quantifiable measure of performance over time for a specific objective. KPIs provide targets for teams to shoot for, milestones to gauge progress, and insights that help people across the organization make better decisions. From finance and HR to marketing and sales, key performance indicators help every area of the business move forward at the strategic level.

Don’t just measure. Measure what matters.
Download the KPI Planning Guide to learn:
- 10 steps to strong KPIs
- Which questions help you define your KPIs
- 170 KPI examples and templates
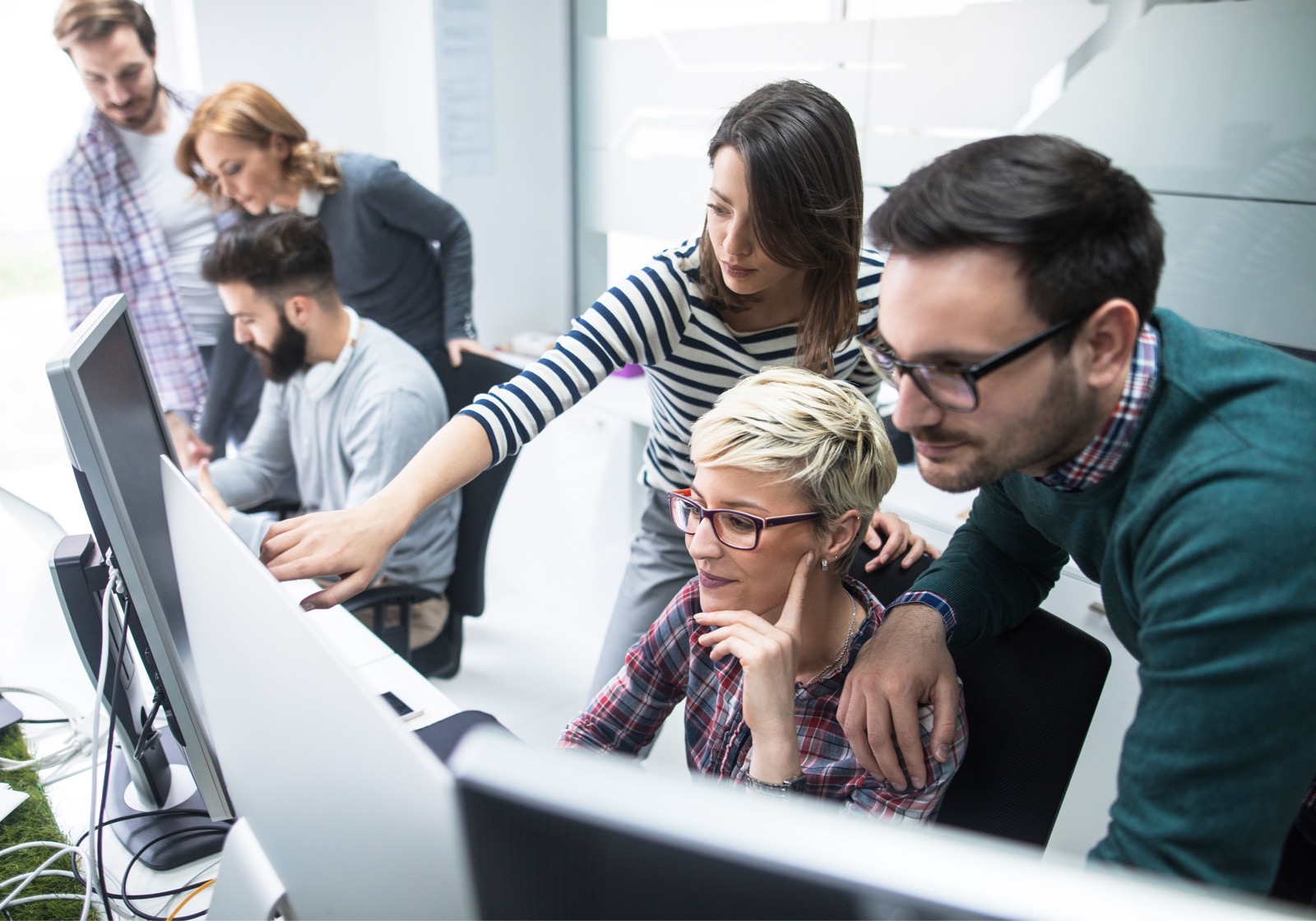
Qlik (Attunity) es reconocido en el Cuadrante Mágico de Gartner para herramientas de integración de datos.
-
- Gross Profit Margin (and %)
- Operating Profit Margin (and %)
-
- Net Profit Margin (and %)
- Operating Expense Ratio
-
- Working Capital Ratio
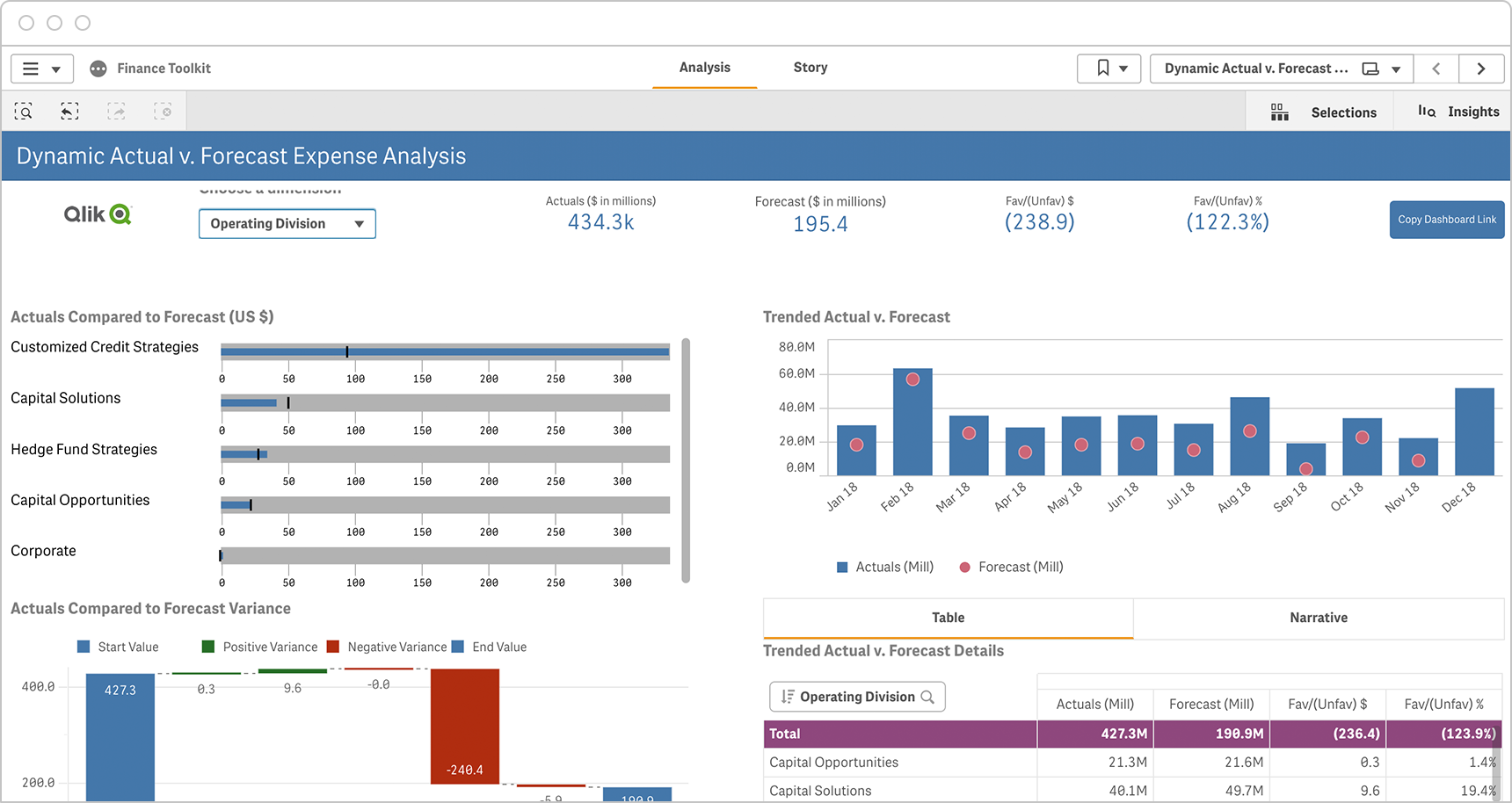
Sales
Ensure your teams are meeting sales targets by tracking and regularly reviewing sales key performance indicators, including those for leads, opportunities, closed sales and volume. Here are some examples of KPIs for sales teams:
-
- New Inbound Leads
- New Qualified Opportunities
-
- Total Pipeline Value
- Sales Volume by Location
-
- Average Order Value
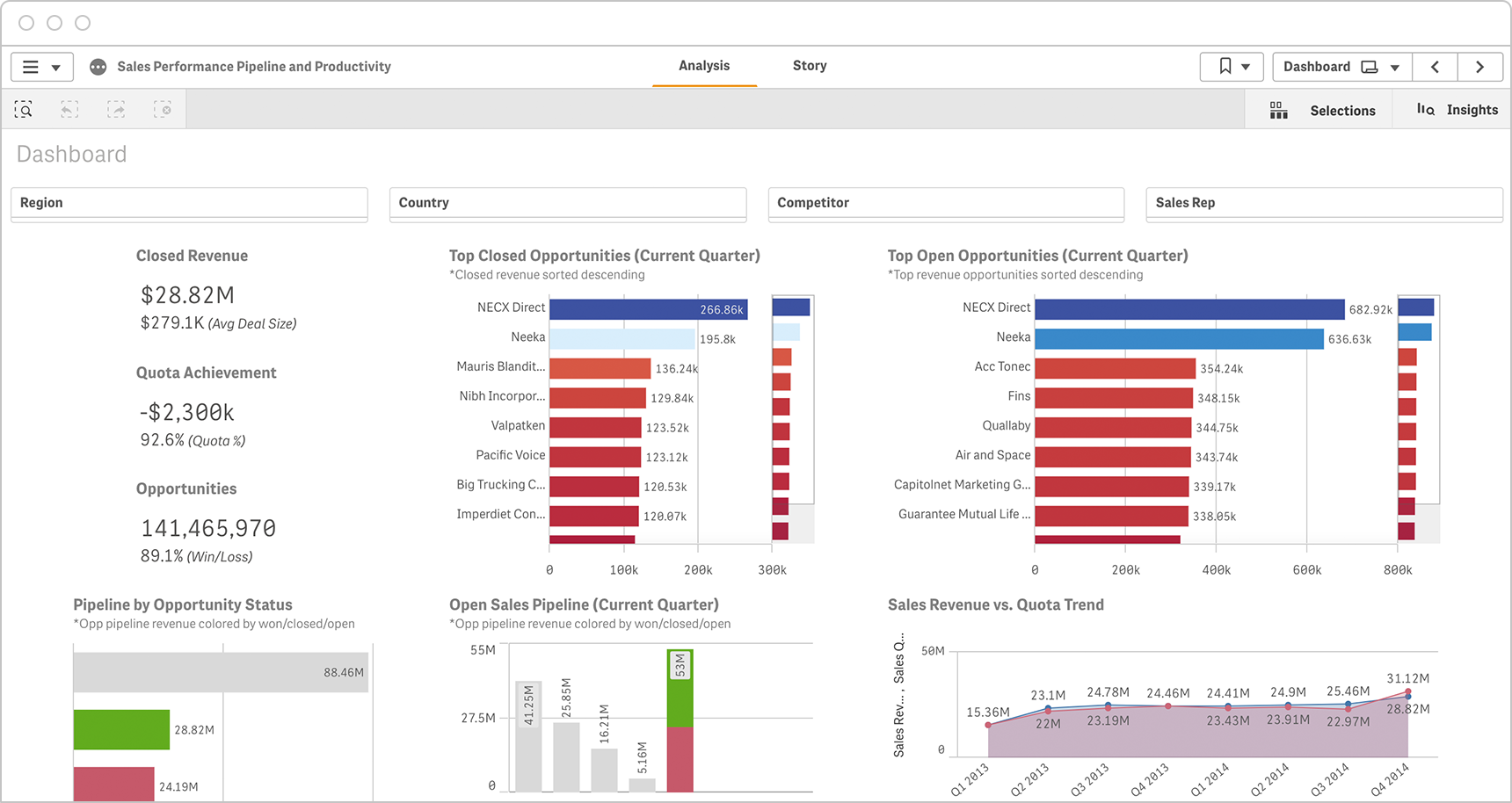
Marketing
Get a handle on marketing spend, conversion rates and other indicators of marketing success by clearly defining key performance indicators and aligning them with your organization’s strategic goals. Here are a few marketing KPIs to get you started.
-
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs)
- Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs)
-
- Conversion Rates (For Specific Goals)
- Social Program ROI (By Platform)
-
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Learn more about Marketing KPIs
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
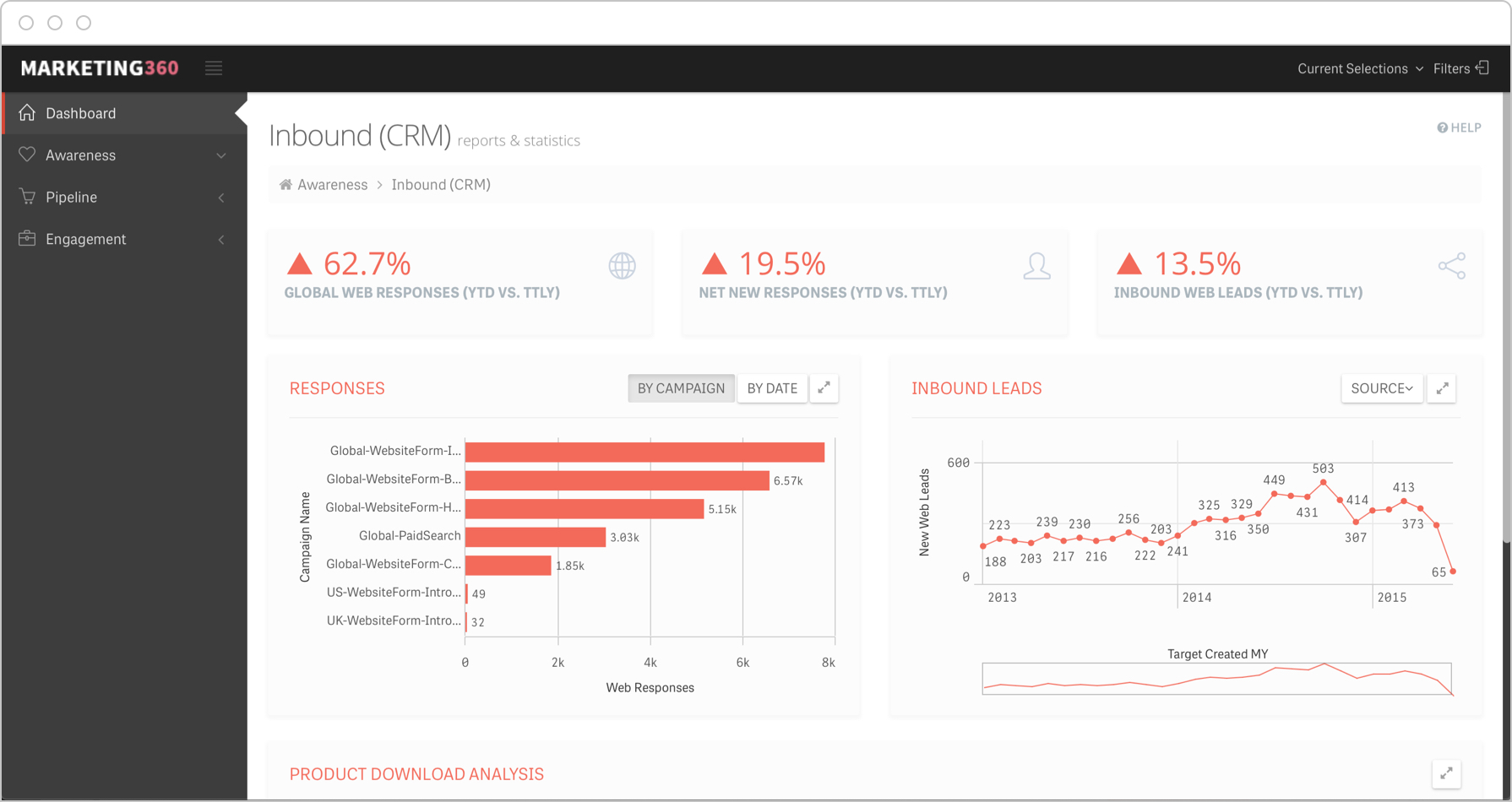
IT Key Performance Indicators
From support tickets to server downtime, IT key performance indicators can help keep teams accountable and alert them to any potential issues coming down the line. KPIs for IT teams could include targets like the following:
-
- Total Support Tickets
- Open Support Tickets
-
- Ticket Resolution Time
- Security Related Downtime
-
- IT Costs vs Revenue
- Reopened Tickets
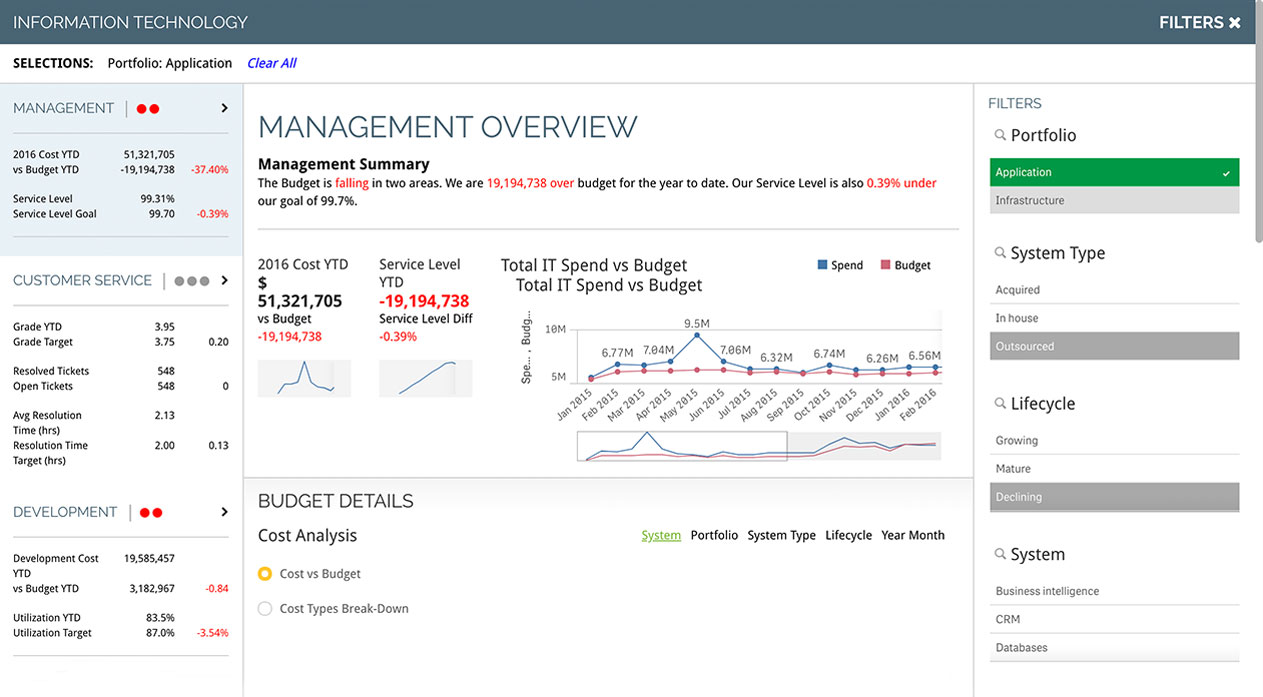
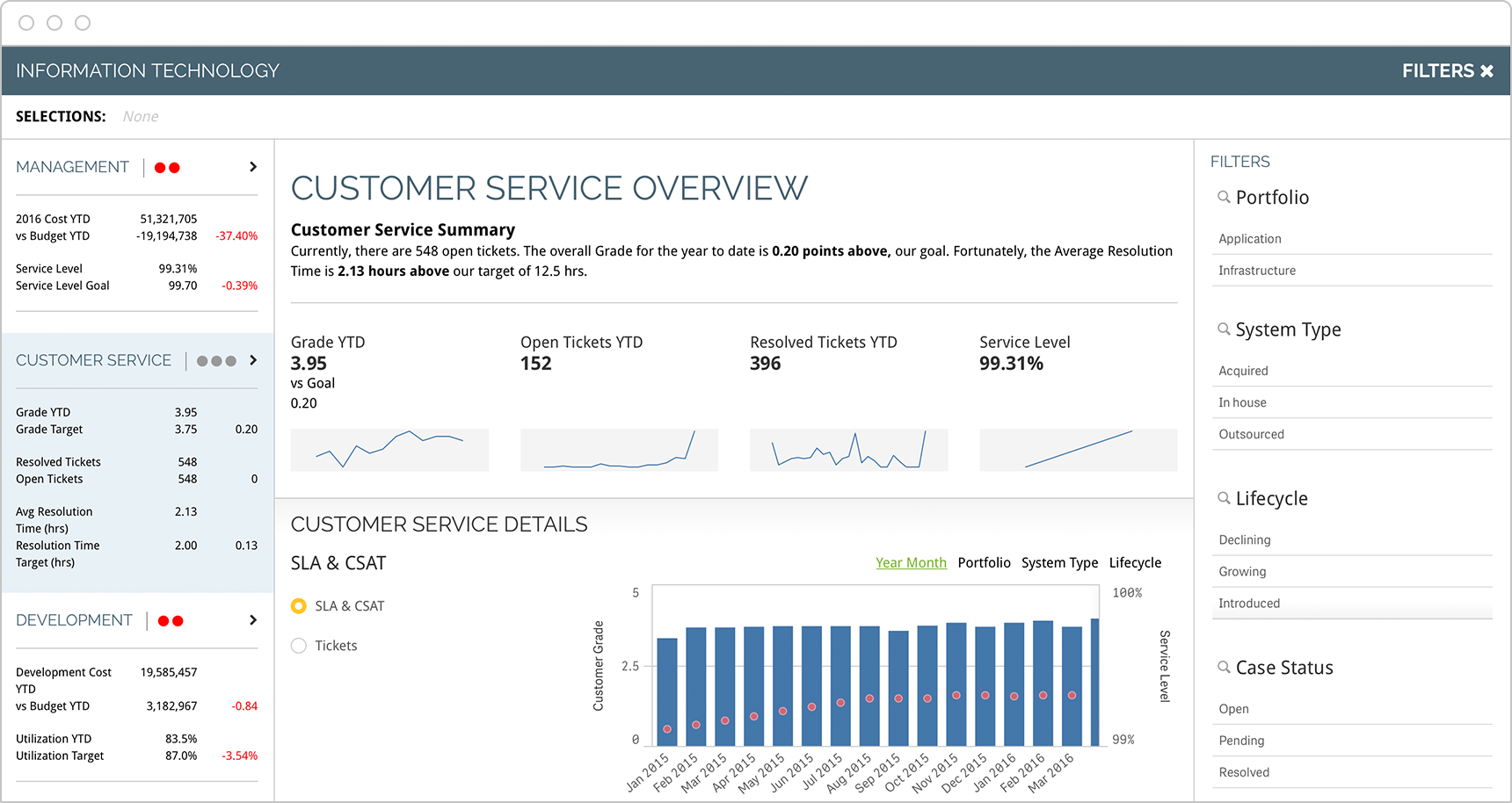
Customer Service
Customer service leaders should track progress related to customers, employees and finances. In addition, key performance indicators should cover both short- and long-term targets, including support response times, customer satisfaction and others that help reach service objectives.
-
- First Contact Resolution Rate
- Average Response Time
-
- Most Active Support Agents
- Cost Per Conversation
-
- Customer Effort Score
FAQs
-
KPI stands for key performance indicator.
-
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are targets that help you measure progress against your most strategic objectives. While organizations can have many types of metrics, KPIs are targets that are “key” to the success of your business.
-
Key performance indicators can be either strategic or operational, and apply to specific business units. For example, finance tracks revenue growth rate and net profit margin, sales measures net sales and sales by region, customer service tracks Net Promoter Score and average resolution time, and marketing might measure traffic-to-lead ratio and cost per lead. Operational key performance indicators could include order fulfillment time and time to market.
-
There are many factors to consider as you develop your key performance indicators (KPIs). Here are some to keep in mind: Define how they will be used, tie them to strategic goals, keep them SMART (specific, measurable, attainable and time-bound), make them understandable, adjust them as needed, and take care only to measure the most important things.
-
While every organization is different, there are a few ways to create high-performing key performance indicators: include a balance of leading and lagging indicators, create a KPI-driven culture by increasing data literacy, and regularly review and adjust your key performance indicators as your audience, market and business change.
